Have you ever felt frustrated by claim denials, delayed payments, or the constant struggle to keep your practice financially stable?
If you’re running a healthcare practice, you know how overwhelming the billing process can be.
Medical billing and coding might not be the first thing you think about when managing your practice, but they’re absolutely essential.
Without them, claims wouldn’t get processed properly, payments would be delayed, and your revenue cycle could spiral into chaos.
In this article, we’ll explain how medical billing and coding work together, why they’re critical for your practice’s financial health, and the tools and strategies that can make them more efficient.
At Cadence Collaborative, we’ve seen how simplifying these processes can transform practices like yours—and we’ll show you how it all works.
What Exactly Is Medical Billing and Coding? How Does It Work?
Medical coding is like turning a patient’s health story into a universal language.
Every time you visit a doctor, whether it’s for a routine check-up, an X-ray, or something more complex, there’s a record of what happened.
Coders take that information (like diagnosis, treatments, or any procedures performed) and assign it specific codes.
These codes come from standardized systems like ICD-10 for diagnoses or CPT for procedures.
Think of it as creating a shorthand version of your visit that everyone in the healthcare system can understand.
Once the coding is done, medical billing takes over. This is where those codes are used to create a claim, a sort of “invoice” that gets sent to the insurance company.
The biller makes sure everything is accurate and submits the claim so the provider can get paid.
They also handle any follow-ups if the claim gets denied or if there’s an issue with payment. Finally, they figure out what part of the bill your insurance covers and what part (if any) you’re responsible for paying.
Here’s how it all works together: coders focus on making sure the medical records are translated into accurate codes, while billers use those codes to handle the financial side of things.
Together, they ensure that healthcare providers get paid on time, patients aren’t overcharged, and insurance companies can process claims efficiently.
How Do Medical Billing and Coding Work Together?
Medical billing and coding are two sides of the same coin, working together to keep the healthcare system running smoothly.
Coders start by translating a patient’s medical records into standardized codes that represent diagnoses, treatments, and procedures.
Once the coding is complete, billers step in to use those codes to create insurance claims and patient invoices.
This is where the two processes overlap, they rely on each other to ensure claims are accurate and complete.
Coders provide the foundation with precise codes, while billers make sure those codes translate into proper payments from insurance companies and patients.
Together, they form the backbone of the healthcare revenue cycle, ensuring providers get paid on time and patients are billed correctly.
Without this teamwork, claim errors, delays, or denials could disrupt the entire system.
Key Terms in Medical Billing and Coding
Medical billing and coding can feel like a different language sometimes, but knowing a few key terms can make things much easier to understand.
What Is Allowed Amount in Medical Billing?
The allowed amount is the maximum amount your insurance company will pay for a specific medical service. It’s like a pre-agreed price between your insurance and your doctor or hospital.
For example, if your doctor charges $200 for a visit but the allowed amount is $150, your insurance will only consider $150 when calculating what they’ll pay.
If you’re seeing an in-network provider, you’ll usually just pay your share (like a co-pay or deductible).
But if it’s an out-of-network provider, you might have to pay the difference between what they charge and what your insurance allows, this is called balance billing.
What Is a Superbill in Medical Billing?
A superbill is basically a detailed receipt that you get from a doctor who doesn’t bill your insurance directly.
It lists all the services you received, along with their costs and codes that insurance companies use to process claims.
If you go to an out-of-network provider, you can use the superbill to file a claim with your insurance company and ask for reimbursement.
Think of it as the paperwork that helps you get some of your money back!
What Is EOB in Medical Billing?
An Explanation of Benefits (EOB) is like a report card from your insurance company after you’ve had medical care.
It tells you what was billed, how much your insurance covered, and what’s left for you to pay (if anything). The EOB isn’t a bill, it’s just an explanation of how everything was handled.
For example, it might say something like: “Your doctor charged $200, we covered $150 (the allowed amount), and you owe $50.”
It also explains why something might not be covered, so it’s worth reviewing carefully.
How Does the Medical Billing Process Work?

The medical billing process is a step-by-step system that ensures healthcare providers get paid for their services while patients are billed correctly. Here’s how it works:
- Patient Registration: It all begins when a patient schedules an appointment. During registration, the provider collects personal and insurance information, which is then verified to confirm coverage and benefits.
- Medical Coding: After the patient’s visit, medical coders translate the doctor’s notes into standardized codes for diagnoses (ICD-10), procedures (CPT), and any additional services. These codes are essential for creating an accurate claim.
- Claim Submission: Using the codes, billers prepare a claim that outlines what services were provided and their associated costs. This claim is then submitted to the patient’s insurance company, either directly or through a clearinghouse that checks for errors before sending it forward.
- Adjudication: Once the insurance company receives the claim, they review it in a process called adjudication. They determine whether the claim is valid, how much they’ll pay based on the patient’s plan, and if any part of the cost is the patient’s responsibility. Claims can be approved, denied, or sent back for corrections.
- Payment Processing: If approved, the insurance pays its share to the provider, and any remaining balance—like co-pays or deductibles—is billed to the patient.
- Follow-Up: For denied or unpaid claims, billers work with insurance companies to resolve issues by correcting errors or providing additional documentation. Appeals may also be filed if necessary.
How Does Claim Submission Work in Medical Billing?
Claim submission is when billers send a detailed request for payment to an insurance company after services are provided.
The claim includes patient information, diagnosis and procedure codes, and costs for each service.
It can be submitted directly to the insurer or through a clearinghouse that checks for errors before forwarding it.
What Is Adjudication in Medical Billing?
Adjudication is how insurance companies review claims to decide whether they’ll pay and how much.
They check if the claim meets their requirements, verify coverage under the patient’s plan, and calculate payment based on pre-negotiated rates (the allowed amount).
If there are issues, like missing information or uncovered services, the claim may be denied or sent back for corrections.
Medical Coding Systems Explained
Medical coding might sound complicated, but it’s really just a way to turn medical information into a universal “language” that everyone in healthcare can understand.
These codes help doctors, hospitals, and insurance companies communicate clearly about what happened during a patient’s visit.
Let’s look at the three main coding systems—CPT, ICD, and HCPCS—and why they’re so important.
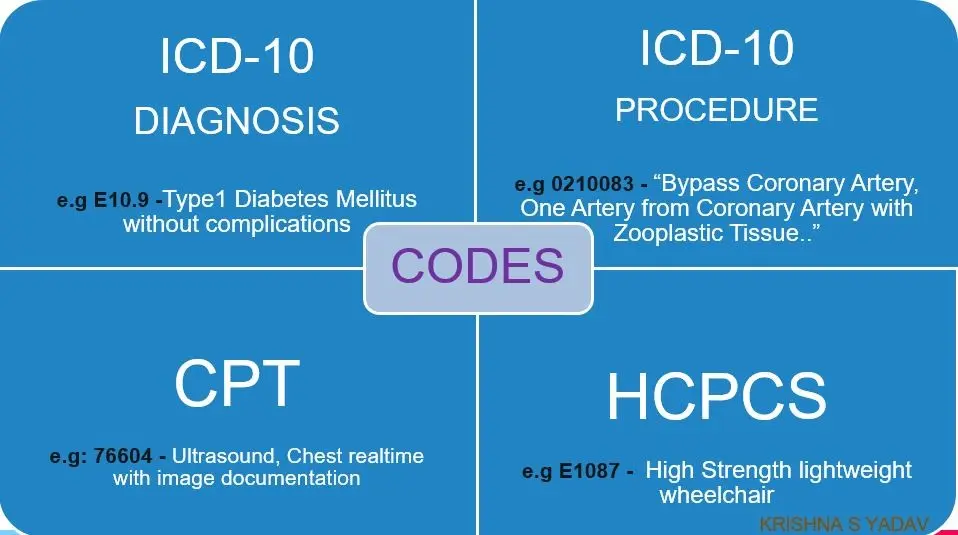
Image Source: Healthcare Claims: Diagnosis and Procedure Codes (ICD-10,CPT,HCPCS)
What Are CPT Codes?
CPT codes (Current Procedural Terminology) are used to describe the specific services or procedures a healthcare provider performs. Think of them as the “what” behind your visit.
Did you get an X-ray? There’s a CPT code for that. Did your doctor perform surgery? There’s a code for that too.
These codes are super detailed and even include modifiers—extra bits of information to explain things like if the procedure was done twice or on a specific part of the body.
CPT codes are especially important for insurance billing because they tell insurers exactly what they’re paying for.
What Is ICD in Medical Coding?
ICD codes (International Classification of Diseases) explain why you needed care. They represent diagnoses or reasons for your visit, like strep throat, a sprained ankle, or diabetes.
For example, if you go to the doctor with flu symptoms, there’s an ICD code that says, “This patient has the flu.”
These codes are updated regularly to keep up with new medical discoveries and treatments.
They’re not just for billing, they also help track health trends worldwide, like how many people are diagnosed with certain conditions each year.
What Are HCPCS Codes?
HCPCS codes (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System) cover things that CPT codes don’t, like medical equipment, supplies, or services outside of a doctor’s office.
For instance, if you need crutches after an injury or an ambulance ride to the hospital, there’s an HCPCS code for that.
In short, these three systems work together like puzzle pieces:
- CPT tells what was done.
- ICD explains why it was done.
- HCPCS covers extra items or services.
Common Challenges in Medical Billing and Coding
Medical billing and coding might seem like a straightforward process, but it comes with its fair share of challenges.
From claim denials to keeping up with ever-changing regulations, billers and coders face many obstacles that can slow down payments and create headaches for healthcare providers.
Why Do Claims Get Denied in Medical Billing?
Claims can get denied for many reasons, but the most common culprits are errors, missing information, or failure to follow insurance rules. Here are a few examples:
- Incorrect Patient Information: Something as small as a misspelled name, wrong date of birth, or outdated insurance details can cause a claim to be rejected. It’s like trying to cash a check with the wrong name on it—it just won’t work.
- Missing Prior Authorization: Some treatments or procedures require approval from the insurance company before they’re done. If this step is skipped, the claim will likely be denied, even if the service was medically necessary.
- Inadequate Documentation: If the medical records don’t clearly show why a procedure was needed or what was done, insurers may deny the claim. For example, if a diagnosis code doesn’t match the treatment provided, it raises red flags.
- Missed Deadlines: Every insurance company has its own timeline for submitting claims—some as short as 90 days after the service. Missing these deadlines can result in automatic denials.
What Are Common Errors in Medical Coding?
Medical coding is all about precision, but even tiny mistakes can lead to big problems. Here are some frequent errors coders face:
- Using Outdated Codes: Medical codes are updated regularly. Using an old code that’s no longer valid can result in claim rejections or underpayments.
- Upcoding or Undercoding: Upcoding means billing for a more expensive service than what was provided (which can lead to audits or fines), while undercoding means not fully capturing the complexity of care (resulting in lost revenue).
- Unbundling Codes: Sometimes multiple services should be billed together under one code. If coders separate them unnecessarily (unbundling), it can trigger denials or accusations of overbilling.
- Missed Modifiers: Modifiers add extra details to codes, like whether a procedure was repeated or done on a specific body part. Forgetting to include them can cause confusion and payment delays.
These challenges highlight just how detail-oriented medical billing and coding must be.
Whether it’s ensuring accurate patient information, staying up-to-date on coding changes, or double-checking documentation, every step matters.
By addressing these issues proactively, billers and coders can help healthcare providers avoid delays and get paid faster—keeping everything running smoothly!
Understanding Denials and Appeals
Navigating claim denials can be frustrating, but understanding why they happen and how to appeal them can make the process much smoother. Let’s break it down in simple terms.
What Is a Denial in Medical Billing?
A denial happens when an insurance company processes a claim but decides not to pay for it. This is different from a rejection, which occurs when a claim is sent back due to errors before it’s even processed. Denials can happen for many reasons, such as:
- Missing or Incorrect Information: A typo in the patient’s name, date of birth, or insurance details can trigger a denial.
- Lack of Prior Authorization: Some procedures require approval from the insurance company beforehand. If this step is missed, the claim may be denied.
- Medical Necessity Issues: If the insurer doesn’t believe the service was necessary based on their criteria, they might deny the claim.
- Coding Errors: Using outdated or incorrect codes can lead to problems.
- Coverage Problems: Services not covered under the patient’s plan or expired insurance policies are common reasons for denials.
How Do You Appeal a Denied Claim?
Appealing a denied claim is like asking the insurance company to take another look and reconsider their decision. Here’s how you can do it:
- Review the Denial Notice: Carefully read the explanation of why the claim was denied. This will help you understand what went wrong and what needs to be fixed.
- Gather Documentation: Collect all relevant documents that support your case, such as medical records, prior authorizations, and correspondence with the insurer.
- Fix Any Errors: If there was a mistake in coding or patient information, correct it before moving forward.
- Write an Appeal Letter: Draft a clear and concise letter explaining why the denial should be reconsidered. Include all supporting evidence and reference specific policy details if applicable.
- Submit and Follow Up: Send your appeal to the insurance company and track its progress. Don’t hesitate to follow up regularly to ensure it’s being reviewed.
- Learn from the Process: Whether your appeal is approved or denied, take note of what caused the issue so you can prevent similar problems in the future.
Essential Tools for Medical Billers and Coders
Medical billing and coding can get pretty complex, but the right tools make everything much easier.
From software that tracks patient records to platforms that help manage claims, these tools are essential for keeping things organized and running smoothly.
What Software Do Medical Billers Use?
Medical billers rely on a variety of software to handle their tasks. Here are some examples of tools that make their work faster and more accurate:
- Medical Billing Software: Platforms like AdvancedMD or DrChrono automate billing processes, from checking insurance eligibility to tracking payments. These tools reduce manual errors and speed up reimbursements.
- Coding Software: Coders use tools like Find-A-Code or TruCode to look up the latest ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes. These platforms ensure accuracy by flagging potential errors before claims are submitted.
- Claims Management Systems: Tools like CollaborateMD help track claims from submission to payment. They alert billers about denials or issues so they can resolve them quickly.
- Practice Management Software: This all-in-one tool helps with scheduling appointments, managing patient records, and processing claims.
Examples include Kareo and PracticeSuite, which streamline administrative tasks and improve workflow.
These tools not only enhance accuracy but also optimize the financial performance of healthcare practices by reducing delays and improving cash flow.
Skilled medical billers are essential to fully leverage these technologies, ensuring smooth operations and maximizing reimbursements.
How Does EMR Help With Medical Billing?

Electronic Medical Records (EMR) systems are like digital filing cabinets for patient information, storing everything from medical history and diagnoses to treatments.
They make it easy for billers and coders to access accurate details when creating claims, reducing typos or missing information that could lead to denials.
Since providers document services in real-time, EMRs speed up claims processing by giving coders instant access to the data they need.
Many EMRs also include built-in checks to ensure documentation matches billing codes, helping providers stay compliant and avoid audits or penalties.
For instance, if a doctor documents a diagnosis but forgets to include a related procedure code, the EMR can flag the issue before the claim is submitted.
Even with great tools like EMRs and billing software, managing everything can still feel overwhelming. That’s where Cadence Collaborative comes in.
We’re here to help simplify your workflow, improve accuracy in your billing processes, and make sure you’re getting the most out of your tools.
Why Choose Cadence Collaborative for Your Billing and Coding Needs?
Managing medical billing and coding doesn’t have to be a headache. At Cadence Collaborative, we make it easy.
With our expertise, we handle complex claims, reduce denials, and ensure you get paid faster, all while staying compliant with ever-changing regulations.
Our focus is on maximizing your revenue and simplifying your workflow, so you can focus on what matters most: your patients.
Let us take the stress out of billing and coding. Contact us today at (401) 743-2428 to see how we can help your practice thrive!